
BILBERRY
🌿 What “Bilberry” means — the plant & extract basics
- “Bilberry” refers to the fruit of the plant Vaccinium myrtillus.
- Many NZ supplements use “bilberry extract (fruit)” rather than raw fresh fruit.
- Extracts are often standardised — meaning the manufacturer ensures a certain concentration of “active compounds” per dose.
✅ The Key Active Ingredient: Anthocyanins / Anthocyanidins
- The most important bioactive components in bilberry are anthocyanins (or anthocyanidins / anthocyanosides / flavonoids). These pigments give bilberry its deep blue-purple colour.
- These anthocyanins are strong antioxidants — meaning they help neutralise free radicals and oxidative stress in the body.
- Because of that antioxidant activity, bilberry is often promoted for eye health, blood vessel / capillary support, circulation, and general antioxidant protection.
For example: in a NZ supplement sold as “Bilberry Fruit” by a supplier, the extract is “standardised to 25% anthocyanins” — meaning 25% of the extract mass is anthocyanins.

BLUEBERRY
🍇 What are the main “key ingredients” in Blueberries
Here are the nutrients and bioactive compounds that make blueberries special.
✅ Basic Nutrients (Vitamins, Minerals, Fiber, Water)
- Blueberries are low in calories and fat, but provide healthy fiber, water, some carbohydrates, a little protein.
- They contain vitamins such as Vitamin C, Vitamin K, and small amounts of Vitamin A, some B‑group vitamins, minerals (e.g. manganese, potassium, magnesium).
- The fiber helps with digestion, and vitamins + minerals support general health (immune system, skin, bones, etc.).
🌿 Bioactive Compounds & Antioxidants (“Phytochemicals”)
The most important — and often most beneficial — components in blueberries are plant compounds rather than basic vitamins/minerals.
- Anthocyanins — These are pigments that give blueberries their deep blue / purple colour. They are powerful antioxidants and are thought to be largely responsible for many of blueberries’ health-promoting effects.
- Flavonoids (including flavonols, flavan‑3‑ols, etc.) — Blueberries also contain other flavonoids (like quercetin, myricetin, catechins) and polyphenols. These compounds have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, cardiovascular‑protective, and possibly neuroprotective effects.
- Polyphenols & phenolic acids / compounds — Beyond anthocyanins and flavonoids, blueberries contain various phenolic compounds (e.g. tannins, organic acids) that contribute to antioxidant capacity and potential health effects.

COLOSTRUM
Colostrum is often highlighted as a key ingredient in various health supplements, particularly for immune support and gut health. The key active components in colostrum include:
- Immunoglobulins (IgG, IgA, IgM) – These are antibodies that help support the immune system.
- Lactoferrin – A protein with antibacterial and antiviral properties.
- Growth Factors (IGF-1, TGF-β) – Support tissue repair and gut health.
- Proline-Rich Polypeptides (PRPs) – Help modulate the immune response.
- Vitamins & Minerals – Including vitamin A, vitamin E, zinc, and selenium.
In New Zealand, colostrum is typically sourced from grass-fed dairy cows, which are prized for high-quality bioactive components due to the clean, pasture-based environment.

EVENING PRIMROSE OIL
Evening Primrose Oil (EPO) supplements are commonly used for skin, hormonal, and inflammatory support. The key active ingredient in Evening Primrose Oil is:
- Gamma-Linolenic Acid (GLA) – an omega-6 fatty acid that supports:
- Hormonal balance (especially for PMS and menopause symptoms)
- Skin health (eczema, dryness, and inflammation)
- Anti-inflammatory effects throughout the body
- Linoleic Acid – another essential omega-6 fatty acid that helps maintain healthy skin and cell function.
New Zealand EPO is usually cold-pressed from the seeds of the evening primrose plant to preserve the delicate fatty acids.

Glucosamine
Glucosamine is a popular ingredient in joint health supplements. The key active component is:
- Glucosamine Sulfate or Glucosamine Hydrochloride – an amino sugar that helps:
- Support cartilage structure
- Maintain joint flexibility
- Reduce joint pain and stiffness, especially in osteoarthritis
- Sometimes combined with:
- Chondroitin – for additional cartilage support
- MSM (Methylsulfonylmethane) – for anti-inflammatory and joint comfort benefits
New Zealand glucosamine is typically sourced from shellfish (shrimp, crab) or fermentation processes for vegetarian-friendly versions.

GREEN MUSSEL
Green-Lipped Mussel (Perna canaliculus) is widely used in supplements for joint and overall health. The key active components include:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids (EPA & DHA) – support cardiovascular health and reduce inflammation.
- Unique Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) – such as chondroitin and hyaluronic acid, which help maintain cartilage and joint flexibility.
- Proteins & Peptides – may support tissue repair and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Minerals – including zinc, magnesium, and selenium for overall health.
Benefits commonly associated with New Zealand Green-Lipped Mussel supplements:
- Reduces joint pain and stiffness, especially in arthritis
- Supports mobility and cartilage health
- Anti-inflammatory effects throughout the body
New Zealand Green-Lipped Mussels are sustainably harvested from clean coastal waters, which preserves the bioactive compounds.

MILKTHISTLE
MILK THISTLE – Key Ingredient
Silymarin
- A complex of flavonolignans (mainly silibinin, silychristin, silydianin)
- The main bioactive ingredient responsible for liver-protective effects
What Silymarin Does
- Liver detox support
- Helps regenerate liver cells
- Protects liver from toxins (alcohol, medications, pollution)
- Powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity
- Supports healthy digestion
Common Forms in New Zealand Supplements
- Milk Thistle Extract (standardised to 70–80% silymarin)
- Sometimes combined with:
- Dandelion root
- Artichoke extract
- Turmeric (curcumin)
- Globe artichoke
Popular Uses
- General liver health
- Fatty liver support
- Detox / cleansing
- Supporting digestion after heavy meals or alcohol

LANOLIN
Lanolin is a common ingredient in skincare and personal care products. The key components and functions are:
- Wool Fat (Lanolin Alcohols & Esters) – acts as an emollient, forming a protective barrier on the skin to lock in moisture.
- Fatty Acids – such as cholesterol, palmitic acid, and oleic acid, which help nourish and soften skin.
- Hydrating Properties – attracts water and keeps skin hydrated, making it especially useful for dry or sensitive skin.
- Skin Barrier Support – helps protect skin from environmental damage and irritation.
Uses in New Zealand products:
- Moisturizers and creams
- Lip balms and ointments
- Baby skincare products
- Healing balms for dry or cracked skin
New Zealand lanolin is typically refined from sheep wool, often from grass-fed sheep, making it high-quality and hypoallergenic.

LUTEIN
✅ What Lutein Is
Lutein is a carotenoid, specifically a xanthophyll, found in leafy green vegetables and some fruits.
The body cannot produce lutein, so it must come from food or supplements.
🌿 Key Active Ingredients / Components in Lutein
1. Lutein (main carotenoid)
- Acts as a powerful antioxidant
- Helps protect the eyes from blue light and oxidative stress
2. Zeaxanthin (often included together)
- Works with lutein to support macular health
- Helps filter harmful blue light
👁️ Main Health Benefits
Eye Health
- Supports the macula and retina
- Helps reduce the risk or progression of Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
- May lower the risk of cataracts
- Protects eyes from blue light exposure
Antioxidant Protection
- Reduces oxidative stress in cells
- Helps protect against age-related cell damage
Brain Health (possible benefit)
- Some research suggests lutein may support cognitive function.
🇳🇿 Lutein in New Zealand Supplements
Recommended to take with a meal containing fat, because lutein is fat-soluble
Usually extracted from marigold flowers (Tagetes erecta)
Often combined with Zeaxanthin, and sometimes:
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin E
- Selenium
- Zinc
- Commonly found in eye-health formulas

NONI
- Noni is the fruit of Morinda citrifolia, a tropical plant widely used in traditional medicine across the Pacific, Southeast Asia, and Polynesia.
- In New Zealand many noni-based products — juices or capsules — use Noni fruit (dried/powder or juice) as their base.
✅ Key Bioactive Components of Noni
Noni contains a variety of nutrients and plant compounds that may contribute to its health effects. Main bioactive ingredients include:
- Vitamins — especially Vitamin C.
- Minerals — e.g. potassium, calcium, magnesium, iron, etc.
- Amino acids / proteins — Noni juice/powder contains some proteins and amino acids.
- Phytochemicals / plant compounds — this is probably the most important category. These include:
- Phenolics, flavonoids, iridoids, anthraquinones — naturally occurring antioxidants & anti-inflammatory agents.
- Specific compounds such as scopoletin, ursolic acid, damnacanthal, xeronine/proxeronine, and others.
- Polysaccharides (complex carbohydrates) — thought to contribute to immune-modulating effects.
💡 What These Components Are Thought to Do (Potential Benefits)
Because of the mix of nutrients and bioactive compounds, Noni is sometimes used or marketed for a wide range of potential health-supporting roles:
General nutrition — as a source of some vitamins, minerals, and amino acids, Noni can contribute to overall nutrient intake.
Antioxidant effects — compounds like flavonoids, phenolics, vitamins (especially vitamin C) help neutralize free radicals, which might help reduce cellular damage.
Anti-inflammatory & analgesic (pain-relief) action — some of the phytochemicals (e.g. scopoletin, ursolic acid) have shown anti-inflammatory or pain-modulating properties in studies.
Immune support — vitamins, minerals, antioxidants and polysaccharides might collectively support the immune system.
OMEGA 3
Omega-3 supplements are very popular for heart, brain, and joint health. The key active ingredients are:
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid) – an omega-3 fatty acid that:
- Supports cardiovascular health
- Reduces inflammation
- May improve mood and cognitive function
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid) – an omega-3 fatty acid that:
- Supports brain and eye health
- Important for fetal and infant development
- Helps maintain healthy cell membranes
- ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid) – plant-based omega-3 (less potent than EPA/DHA) found in flaxseed and chia oil.
Sources in New Zealand supplements:
- Fish oil – typically from sustainably sourced fish
- Krill oil – rich in EPA/DHA and phospholipids
- Algal oil – a vegetarian/vegan source of DHA
New Zealand Omega-3 products often highlight sustainability and purity, ensuring low heavy metals and contaminants.

OVINE PLACENTA
Ovine Placenta is used primarily in health and beauty supplements. The key active components include:
- Growth Factors – such as IGF-1 (Insulin-like Growth Factor) which may support skin regeneration, tissue repair, and overall cell renewal.
- Amino Acids & Peptides – building blocks for collagen and elastin, supporting skin elasticity and hydration.
- Vitamins & Minerals – including B vitamins, iron, and trace elements that nourish skin and hair.
- Placental Proteins – thought to promote skin health, reduce wrinkles, and enhance overall vitality.
New Zealand ovine placenta is usually sourced from pasture-raised sheep, ensuring high-quality bioactive components. It is commonly found in:
- Skincare capsules and serums
- Anti-aging supplements
- Hair and nail health products

PROPOLIS
Propolis is a well-known natural immune-support ingredient. The key active components include:
- Flavonoids
- Strong antioxidant and antibacterial compounds
- Main measure of propolis quality (often shown as flavonoid mg or BIO rating)
- Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester (CAPE)
- Supports immune function
- Known for anti-inflammatory and antiviral activity
- Phenolic Acids
- Help fight bacteria and support healing
- Amino Acids, Vitamins & Minerals
- Support overall immune strength
New Zealand propolis is usually sourced from bees feeding on native plants like manuka and kanuka, giving it high bioactive content.
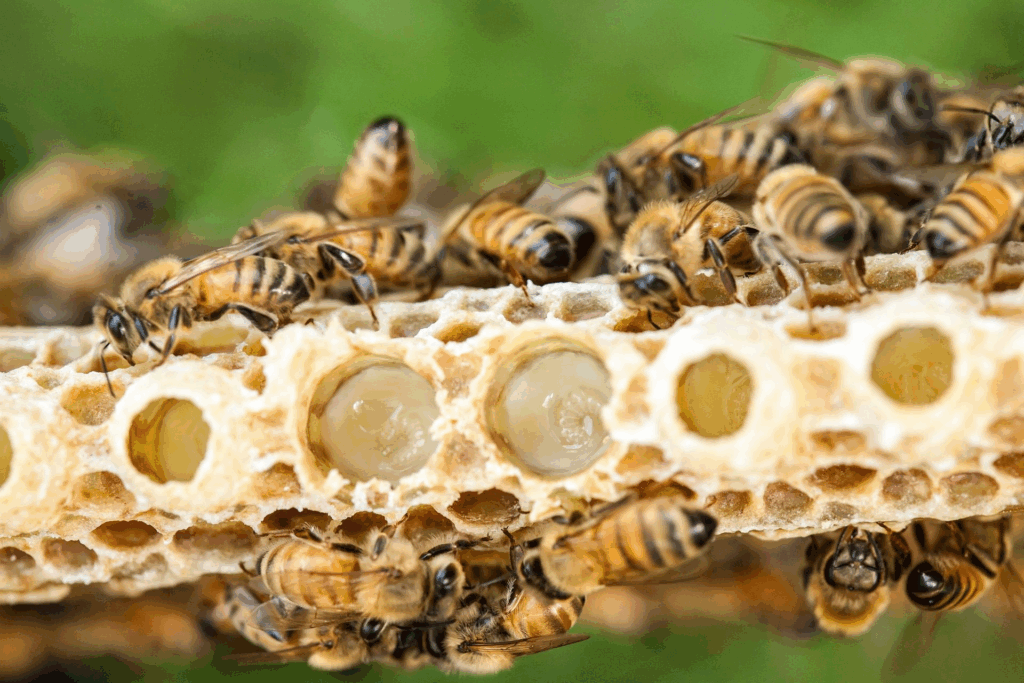

Royal Jelly
Royal Jelly is a nutrient-rich secretion fed to the queen bee.
Key Ingredients / Bioactive Compounds
- 10-Hydroxy-2-Decenoic Acid (10-HDA)
- The signature component of royal jelly
- Supports immune function, skin regeneration, anti-aging effects
- Higher % = higher quality
- Protein Complexes (MRJPs: Major Royal Jelly Proteins)
- Support cell repair and tissue regeneration
- Amino Acids
- Building blocks for skin, immune, and energy support
- Vitamins (B-complex: B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B12)
- Boost metabolism, energy, and skin health
- Minerals – calcium, zinc, iron, potassium
Uses:
✔ Anti-aging skin support
✔ Energy and vitality
✔ Immune support
✔ Hormonal balance (often used by women)
SHARK CARTILAGE
Main Active Components:
- Chondroitin Sulfate
- The most important component.
- Supports joint cushioning, cartilage repair, and reduced inflammation.
- Often used for osteoarthritis and joint stiffness.
- Glucosamine (naturally occurring)
- Helps maintain cartilage structure and joint mobility.
- Works together with chondroitin for joint protection.
- Calcium & Phosphorus
- Natural minerals found in cartilage.
- Supports bone strength and overall skeletal health.
- Collagen Proteins
- Structural proteins that support joint elasticity, tissue repair, and skin health.
- Mucopolysaccharides (GAGs)
- Includes hyaluronic acid-like compounds.
- Helps lubricate joints and reduce inflammation.

SPIRULINA
Spirulina is grown in clean, controlled environments and is known for its purity and nutrient density. Its key active ingredients include:
1. Complete Protein (≈ 60–70%)
- Contains all 9 essential amino acids
- Supports muscle repair, energy, and immune health
2. Phycocyanin (Blue Pigment Antioxidant)
- A powerful antioxidant
- Supports immune function and reduces inflammation
3. Chlorophyll
- Natural detoxifier
- Helps cleanse and alkalize the body
4. Vitamins
- Vitamin B12 (in bioactive form) – supports energy and red blood cells
- Vitamin K – supports blood and bone health
- Vitamin A (beta-carotene) – eye and skin health
5. Minerals
- Iron – energy and oxygen transport
- Magnesium, Calcium, Zinc – cell health and immunity
6. Essential Fatty Acids
- Includes GLA (Gamma-Linolenic Acid)
- Supports skin health and reduces inflammation
7. Antioxidants
- Superoxide dismutase (SOD)
- Helps protect cells from oxidative stress
